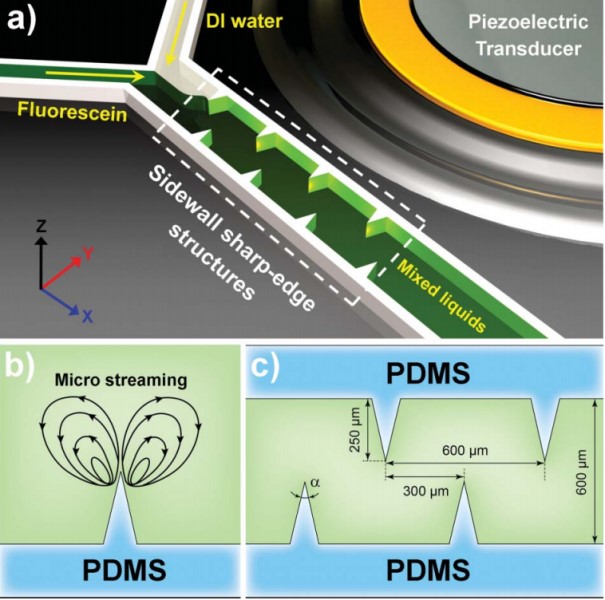
Figure 5: (a) Schematic of the acoustic-based mixing device. This device includes a PDMS microfluidic channel and a piezoelectric transducer. (b) Schematic showing the acoustic streaming phenomenon around the tip of an acoustically oscillated sharp-edge. (c) Schematic showing the design of the channel and sharp-edge.
Rapid and homogeneous mixing inside a microfluidic channel is demonstrated via the acoustic streaming phenomenon induced by the oscillation of sidewall sharp-edges. By optimizing the design of the sharp edges, we achieved excellent mixing performance and fast mixing speed in a simple device, making our sharp-edge-based acoustic micromixer a promising candidate for a wide variety of applications.
References:
https://www.nsf.gov/news/news_summ.jsp?cntn_id=135860&org=NSF&from=news
Po-Hsun Huang, Yuliang Xie, Daniel Ahmed, Joseph Rufo, Nitesh Nama, Yuchao Chen, Chung Yu Chan, and Tony Jun Huang, An acoustofluidic micromixer based on oscillating sidewall sharp-edges, Lab on a Chip, Vol. 13, pp. 3847-3852, 2013. [PDF]
Po-Hsun Huang, Liqiang Ren, Nitesh Nama, Sixing Li, Peng Li, Xianglan Yao, Rosemarie A. Cuento, Cheng-Hsin Wei, Yuchao Chen, Yuliang Xie, Ahmad Ahsan Nawaz, Yael G. Alevy, Michael J. Holtzman, J. Philip McCoy, Stewart J. Levine and Tony Jun Huang, An acoustofluidic sputum liquefier, Lab on a Chip, Vol. 15, pp. 3125-3131, 2015. [PDF]
Po-Hsun Huang, Chung Yu Chan, Peng Li, Yuqi Wang, Nitesh Nama, Hunter Bachman, and Tony J. Huang, A sharp-edge-based acoustofluidic chemical signal generator, Lab on a Chip, accepted, 2018. [PDF]
