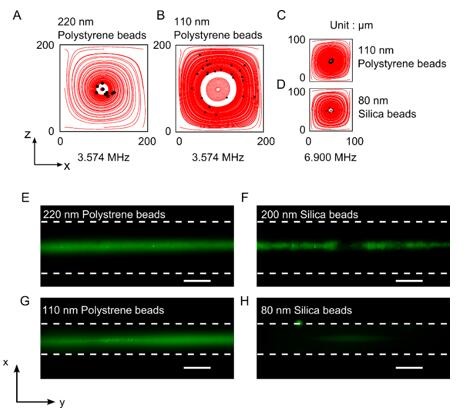
Figure 4: Numerical and experimental results of acoustic enrichment of nanoparticles in the glass capillaries. (A-B) Numerical results of 220 nm and 110 nm polystyrene particles’ trajectories in a glass capillary’s inner cross section with dimensions of 200 µm × 200 µm when SAW with a frequency of 3.574 MHz is applied. (C-D) Numerical results of 110 nm polystyrene particles and 80 nm silica particles’ trajectories in a glass capillary with an inner cross section of 100 µm × 100 µm when SAW with a frequency of 6.9 MHz is applied. (E-F) Top view of the focused 220 nm fluorescent polystyrene particles and 200 nm fluorescent silica particles in a glass capillary with inner cross section of 200 µm × 200 µm when SAW with a frequency of 3.574 MHz was on. (G-F) Top view of focused 110 nm fluorescent polystyrene particles and 80 nm fluorescent silica particles in a glass capillary whose inner cross section is 100 µm × 100 µm when SAW with a frequency of 7.138 MHz was on. The scale bars represent 100 µm. The dashed lines indicate the channel walls.
Focusing and enriching micrometer and nanometer scale objects is of great importance for many applications in biology, chemistry, and medicine. We have developed an acoustofluidic chip that can generate single-vortex acoustic streaming inside a square, glass, capillary through using low-power acoustic waves (only 5V is required). The single-vortex acoustic streaming that is generated, in conjunction with the acoustic radiation force, is able to enrich micrometer, sub-micrometer, and nanometer sized particles in a small volume. With its advantages in simplicity, functionality, and power consumption, the acoustofluidic chip we present here is promising for many point-of-care applications.
References:
https://www.nsf.gov/news/news_summ.jsp?cntn_id=190980&org=NSF&from=news
http://www.nanotech-now.com/news.cgi?story_id=54284
Zhangming Mao, Peng Li, Mengxi Wu, Hunter Bachman, Nicolas Mesyngier, Xiasheng Guo, Sheng Liu, Francesco Costanzo, and Tony Jun Huang, Enriching Nanoparticles via Acoustofluidics, ACS Nano, Vol. 11, pp. 603-612, 2017. [PDF]
Yuchao Chen, Sixing Li, Yeyi Gu, Peng Li, Xiaoyun Ding, Lin Wang, J. Philip McCoy, Stewart J. Levine and Tony Jun Huang, Continuous enrichment of low-abundance cell sample using standing surface acoustic waves (SSAW), Lab on a Chip, Vol. 14, pp. 924-930, 2014.[PDF]
